Die Application Gallery bietet COMSOL Multiphysics® Tutorial- und Demo-App-Dateien, die für die Bereiche Elektromagnetik, Strukturmechanik, Akustik, Strömung, Wärmetransport und Chemie relevant sind. Sie können diese Beispiele als Ausgangspunkt für Ihre eigene Simulationsarbeit verwenden, indem Sie das Tutorial-Modell oder die Demo-App-Datei und die dazugehörigen Anleitungen herunterladen.
Suchen Sie über die Schnellsuche nach Tutorials und Apps, die für Ihr Fachgebiet relevant sind. Beachten Sie, dass viele der hier vorgestellten Beispiele auch über die Application Libraries zugänglich sind, die in die COMSOL Multiphysics® Software integriert und über das Menü File verfügbar sind.
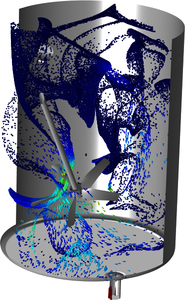
Continuous mixing is used in process equipment to mix components in a single pass. Compared to batch mixing, this operation has the advantage that the tank filling and emptying steps are eliminated, implying that the process can be run without interruptions. A disadvantage of continuous ... Mehr lesen
This example demonstrates the modeling of a sandwiched composite blade made up of carbon–epoxy, glass–vinylester, and PVC foam materials. Three different methods are used to model the sandwich composite structure: Layerwise theory, Equivalent Single Layer (ESL) theory, and a ... Mehr lesen
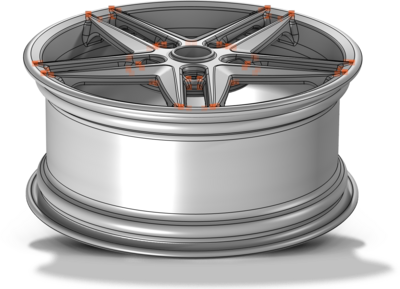
This tutorial shows how to clean an imported CAD geometry using Geometry Cleanup. This helps to improve the mesh and reduce the total number of elements. Mehr lesen
This model computes the fundamental eigenfrequency and eigenmode for a tuning fork that is synchronized from Inventor® via the LiveLink™ interface. The length of the fork is then optimized so that the tuning fork sounds the note A, 440 Hz. Mehr lesen
In diesem Beispiel wird eine Festoxid-Elektrolysezelle modelliert, in der Wasserdampf reduziert wird, um an der Kathode Wasserstoffgas zu bilden, und an der Anode Sauerstoffgas entsteht. Die Stromverteilung in der Zelle ist mit dem kathodenseitigen Stofftransport von Wasserstoff und ... Mehr lesen
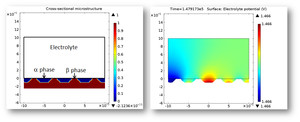
Galvanic corrosion between two different phases (alpha and beta phases) in a metallic (magnesium) alloy is simulated for a representative cross-sectional microstructure configuration. A key feature in the model formulation is the implementation of both anodic and cathodic regions at ... Mehr lesen
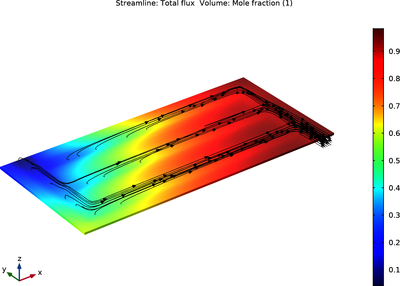
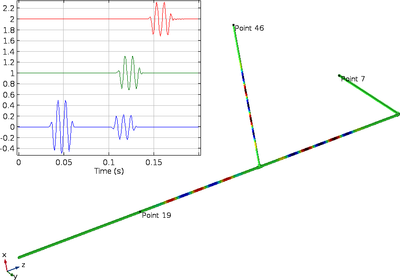
This tutorial shows how to model the propagation of acoustic waves in large pipe systems by coupling the Pipe Acoustics interface to the Pressure Acoustics interface. The tutorial is set up in both the time domain and the frequency domain. 1D pipe acoustics is used to model the ... Mehr lesen
In this example, the dynamics of a hopping hoop is simulated. A rigid rolling ring with a point mass on the perimeter can, under certain conditions, jump up from the surface on which it is rolling. The effects of different parameters like initial velocity and friction are explored. You ... Mehr lesen
This tutorial demonstrates how an electrical circuit model of a MEMS resonator can be derived using the Parameter Estimation feature. The model is a modified Butterworth-Van Dyke circuit created using the Electrical Circuit interface and represents a Thin-Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator ... Mehr lesen
This model, dealing with the current and potential distribution around one pair of electrodes, demonstrates how to synchronize and modify geometry in Solid Edge® by using the LiveLink™ interface with a parametric sweep. Mehr lesen