Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
Reynolds equation is used to analyze fluid flow through small gaps. As such, the solution of Reynolds equation provides critical information for a wide range of tribological problems. In any case where a lubricant resides between two moving surfaces, the Reynolds equation can be used to ... Mehr lesen
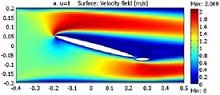
The research team has devised and patented an oscillating, hydro-kinetic power-generating device for use in river and tidal environments. The interaction of water and the designed foil in a straight rectangular turbulent channel is modeled explicitly using two conservation laws: ... Mehr lesen
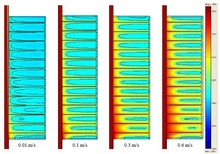
The finite element method applied to the k-epsilon turbulence model is used to investigate the two-stream turbulent mixing layer. Whereas the model is known as one of the most popular of the turbulence models to date, the model has yet to be applied to the classical mixing layer problem ... Mehr lesen
A reaction between chemical species is modeled by a particular reaction pathway, in which one reaction is very fast relative to the other one. The diffusion controlled reactions of these species together with a reaction intermediate are described by a system of three transient reaction ... Mehr lesen
A comparison of the commercial code COMSOL is performed with the bench-mark solutions provided by the literature for a tall, differentially heated rectangular cavity for aspect ratios of 8, 15, 20, and 33. At small Rayleigh numbers the flow is dominated by conduction. As the Rayleigh ... Mehr lesen
The collection efficiency of aerosol particles on a ribbon in a turbulent flow is analyzed using COMSOL Multiphysics. The flow field is solved using Chemical Engineering module and particle tracing plots are obtained using equations of motion including Khan and Richardson drag force. A ... Mehr lesen
In this study, numerical simulations of mixing in turbulent flow, subject to a change in density, are performed. Attention is focused on the binary mixing between two streams of fluid in which a variable density step are formed due to a difference in the temperature. This binary mixing ... Mehr lesen
Mixing is characterized in liquids moving between bubbles when the bubbles are moving down a microfluidic channel. The shape is assumed based on fluid mechanical arguments and experimental observations, and the mixing is characterized for a variety of situations in two and three ... Mehr lesen
This work demonstrated the importance and feasibility of experimental image to simulation workflow. The workflow is successfully applied to a food processing study, where multiphysics and multiscale modeling based on 3D experimental image reconstruction contributes to the preservation of ... Mehr lesen
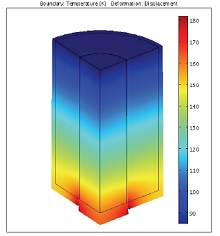
One way of storing thermal energy is through the use of latent heat energy storage systems. One such system, composed of a cylindrical container filled with paraffin wax, through which a copper pipe carrying hot water is inserted, is presented in this paper. It is shown that the physical ... Mehr lesen