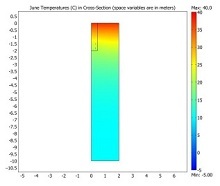
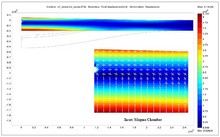
Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
Geothermal heat pumps use the earth as a heat source and sink via a ground heat exchanger (GHX) that consists of a network of buried heat exchange pipes, which can either be installed in vertical boreholes or in shallow horizontal trenches or excavations. The main goal in GHX design is ... Mehr lesen
We present an implementation of the Structural Mechanics module of COMSOL Multiphysics to model the state of stress associated with the emplacement of large volcanic edifices on the surface of a planet. These finite element models capture two essential physical processes: (1) Elastic ... Mehr lesen
To consider effective counter measures against ground water contaminated with dense non-aqueous phase liquids (DNAPLs) such as chlorinated solvents, it is first important to understand the mechanism of their migration in heterogeneous aquifer. In addition, numerical analysis models to ... Mehr lesen
Natural groundwater flow can increase the efficiency of geothermal system. But groundwater flow is not available everywhere. A patented new idea is to use air injection well to create artificial flow in sandy or gritty soils. The governing equations of fluid flow and heat transfer ... Mehr lesen
The bentonite barrier is an essential part of a safe spent fuel repository in granitic bedrock. In this work COMSOL Multiphysics® is used in modelling the Thermal (T), Hydrological (H), Mechanical (M) and Chemical (C) phenomena and processes taking place in a bentonite buffer. Special ... Mehr lesen
Modeling soil water dynamics requires an accurate description of soil hydraulic properties, i.e. the retention and hydraulic conductivity functions. Generally, these functions are assumed to be unchanged over time in most simulation studies. In this paper, we implemented temporal changes ... Mehr lesen
A benchmark study was carried out by the Swiss Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (ENSI) in collaboration with the Laboratory for Waste Management (LES) of the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) in order to evaluate the capabilities of the program COMSOL for the calculation of the transport of ... Mehr lesen
Advances in visualization and discretization of pore structures by means of Computed Tomography, and rapidly increasing computational capabilities, allow numerical modeling of pore-scale fluid flow based on the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations rather than using a macroscopic ... Mehr lesen
The method to derive upscaled expressions for the dispersion coefficients for reactive flow in a porous medium uses a periodic unit cell (PUC), which consists for instance of a spherical grain in a cube, but nothing prohibits defining more complex PUC's. Homogenization leads to a coupled ... Mehr lesen
We combine the potentiality of COMSOL with Monte Carlo optimization procedures, referred to as Simulated Annealing and Genetic Algorithm, in order to analyze and interpret ground deformation measured in active volcanic areas. Through MATLAB® subroutines, we use FE (Finite Element) ... Mehr lesen