Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
Characterization of particles has numerous applications in science and diagnostics. Recently, particle passage through constrained microchannels has been proposed to characterize particles based on their passage velocity. Nevertheless, there is no clear understanding of how the physics ... Mehr lesen
Flexible electronics are temporarily affixed to a rigid carrier such as glass or silicon prior to device fabrication to facilitate robotic handling of the device, but also to allow optical lithography to stay within overlay design registration budget; without the rigid carrier, a ... Mehr lesen
This project utilizes the heat transfer module of the COMSOL Multiphysics environment to model the effects that an ohmic heating probe will have on neural tissue. The model quantifies the thermal impact of active components embedded on a neural micro probe by solving the Penne’s bioheat ... Mehr lesen
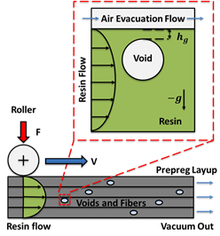
Voids in composite materials can lead to degraded structural performance. The following is a study of voids or bubbles in uncured viscous polymer resin during composites processing. The goal is to determine if voids can successfully migrate towards vacuum pathways, coalesce with the ... Mehr lesen
The rapid increase in power densities of integrated circuits has induced a significant interest in new reliable and high heat flux cooling technologies. The implication of such growth is the increased need for more efficient and more compact cooling mechanisms. Promising research has ... Mehr lesen
A scheme for inductive wireless powering and readout of passive LC sensor is presented. The sensor’s inductor is designed as a planar square coil and is used as the power receiving component. The capacitor is connected directly to the inductor and it was designed as an interdigital ... Mehr lesen
A wireless passive pressure sensor and the measurement system were design and simulated using COMSOL 4.3. The sensor is based on MEMS capacitor attached to a planar inductor for wireless powering and readout. An external coil is used for the measuring system. The pressure to be measured ... Mehr lesen
Electrofluidic transport through a single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) is enhanced by electroosmosis. Electroosmosis is made possible in these devices by the combination of a large slip length within SWCNTs and the interfacial potential at the solution/nanotube interface. A ... Mehr lesen
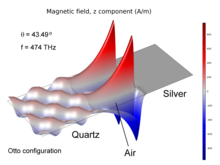
The resonance conditions for surface plasmons are influenced by the type and amount of material on a surface. Full insight into surface plasmon resonance requires quantum mechanics considerations. However, it can be also described in terms of classical electromagnetic theory by ... Mehr lesen
In semiconductor manufacturing, effective cleaning of structures with liquid is one of the most important and potentially difficult process steps. It is important because it remains the cheapest and most cost-effective method to remove particles and residues from the structures in order ... Mehr lesen