Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
The actuation system of the deformable mirror is one of the crucial components of an Adaptive Optics unit. One possible implementation comprehends a linear force motor and a capacitive sensor providing the feedback measure signal. Choosing a magnetic circuit that makes optimum use of the ... Mehr lesen
The ongoing trend towards miniaturization, higher integration as well as cost efficiency will make it necessary to investigate a new assembly method for micro components. In this paper, a novel method of fluidic-based micro assembly is presented. A self-assembly effect which is caused by ... Mehr lesen
The idea of application as a hearing device based on a parasitoid fly, Ormia ochracea has been studied extensively recently. This paper addresses another possible application as an underwater directional sensor. In order to study the feasibility of the application, it is necessary to ... Mehr lesen
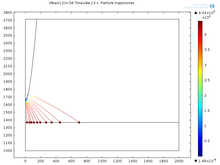
In our recent experiments we are revisiting the topografiner technology for the imaging of surface topography with a resolution of a few nanometers. In these new technique called Near-Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (NFESEM), low-energy electrons are emitted from a ... Mehr lesen
Low-dimensional semiconductor nanostructures, in which charge carriers are confined in a number of spatial dimensions, are the focus of much solid-state physics research, offering superior optical and electronic properties over their bulk counterparts. Both two-dimensional (2D) and zero ... Mehr lesen
The shear mode of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) is preferred to the longitudinal mode owing to its lower acoustic losses in a liquid. However in addition to mass loading, the resonance is also affected by temperature and liquid viscosity. These two parameters can either be sensed ... Mehr lesen
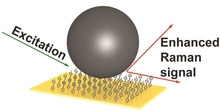
Plasmons, i.e. the collective oscillations of electrons in a metallic nano-structure, lead to strong light scattering, absorption and an enhancement of the local electromagnetic field. In this work, the local electric-field enhancement in a system of dielectric nanoparticles placed ... Mehr lesen
Usually, in integrated circuits, the chip is brazed on leadframe and then, a polymer resin is molded around to create the packaging. On the first hand, the molding process at high temperatures will induce thermomechanical stress on the chip. As the leadframe, the chip and the braze have ... Mehr lesen
Viscous damping has a significant effect on dynamic performance of the resonators operating within fluid. This work is aimed to find the viscous damping for MEMS torsional paddle operating in air. Interaction of moving structure with the fluid requires a complicated and challenging ... Mehr lesen
A COMSOL Multiphysics® simulation was used to simulate the behavior of a micro-membrane (Acoustic Pixel) to be used as a potential acoustic transducer. The MEMS and Piezoelectric devices interfaces were used to simulate such transducer. A four-cantilever spring configuration is initially ... Mehr lesen