Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
The model proposed by Schneider et al., for polymers is herein adapted in order to assess its suitability in elucidating the thixotropic behavior of aluminum alloys. The COMSOL Multiphysics program is employed to solve the inherent coupled mathematical problem, consisting in the ... Mehr lesen
All particles in suspension have a zeta potential, or surface potential. Its measurement is extremely important for predicting the formulation stability across a wide range of industries including food, ink and pharmaceuticals, water purification and medical devices. Zeta potential is ... Mehr lesen
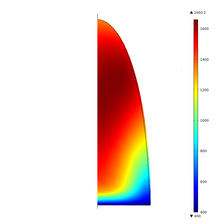
The aim of the study is to predict the formation of porosities in the case of spot laser welding of tantalum. During the interaction, a deep and narrow cavity, called the keyhole, is generated. At the end of the interaction, surface tension provokes the collapse of the keyhole. Gas ... Mehr lesen
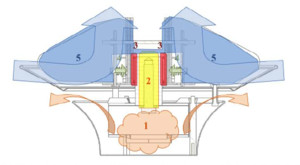
This paper describes a numerical solution method for the simulation of a cold crucible induction melting (CCIM) process involving the coupling of electromagnetic, temperature and turbulent velocity fields. During the CCIM process, the metal charge is contained on a water cooled ... Mehr lesen
In many metallurgical processes metals are (heated and) stirred by an oscillating external magnetic field. The magnetic field induces electric currents in the metal and the currents interact with the magnetic field to create a force, the Lorentz force. For high frequencies induction only ... Mehr lesen
Lorentz Force Velocimetry (LFV) is a non-contact measurement technique used to determine flow rates in electrically conducting fluids by exposing the flow to an external magnetic field and measuring the Lorentz force acting on the magnet system. Typically, for LFV applications real and ... Mehr lesen
An autonomous gas-heater for outdoor environments was selected as a test-case for cogeneration in gas-heaters and stoves, permitting installation and operation without need of an electrical network connection. A thermoelectric generator (TEG) was designed, converting part of produced ... Mehr lesen
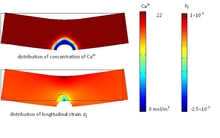
A lixiviation-mechanical coupled model is developed for fiber reinforced concrete within this framework; both the influence of chemical degradation on short and long term mechanical behavior and the influence of mechanical loading on the diffusion coefficient can be considered. The ... Mehr lesen
Electric construction components exposed to alternating high voltage have to withstand a significant amount of thermal loads and, resulting from the changes in Temperature , structural stresses. In order to achieve minimization of these loads, optimizing the geometry can be a helpful ... Mehr lesen
The article deals with the magnetically-supported high-power full-penetration laser beam welding of aluminum. A stationary simulation was conducted accounting for the effects of natural convection, Marangoni convection and solid-liquid phase transition as well as an electromagnetic ... Mehr lesen