Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
An external library, M4Dlib [1], has been developed to solve multiphysics problems coupled to solution thermodynamics. This approach extends the local equilibrium concept[2] to multiphysics modeling by incorporating a full Gibbs energy minimization routine at each numerical node to ... Mehr lesen
The world’s landfills are beginning to fill up due to the growing human population. Landfills require land and there will come a time when there will be no land to be used for landfills. A solution that is gaining attraction is the conversion of traditional “dry-tomb” landfills (used for ... Mehr lesen
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) finds application in many manufacturing processes of microelectronic devices and MEMS as a recent development. It is also useful for preparation of functionalized surfaces in microsensor kind of devices. The phenomena that is studied is deposition of a ... Mehr lesen
The purpose of this work is to show whether an important difference in Lithium solid concentration and electrolyte concentration can be observed in a Lithium-ion battery model, when considering either the Butler-Volmer kinetics or the Tafel kinetics for describing the electrode kinetics ... Mehr lesen
One big challenge for the food industry is to predict and optimize flavors. The Maillard reaction occurs in food matrices containing carbohydrates and proteins under specific operating conditions. The presented research couples thermal and kinetic modeling to the bread baking process, ... Mehr lesen
Reformer and catalytic burners are common components in fuel cell systems, crucial for efficient preparation of fuel and exhaust gases of the fuel cell stack. We intend to show the influence of radiation to the temperature distribution inside of a reformer unit. The model consists of an ... Mehr lesen
The 3D unit cell model approach offers an efficient tool to analyze the influences of geometrical design (channel shape and arrangement, filter length, wall thickness) and filter material properties (permeability, soot loading characteristics) on the performance of ceramic particle ... Mehr lesen
Heap leaching in the mining industry had become a sophisticated practice at least 500 years ago. It is a mineral processing technology whereby piles of crushed Run-of–Mine rock are leached with chemical solutions to extract minerals. The goal of this work is to contribute to the ... Mehr lesen
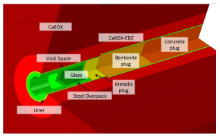
Andra (The French National Radioactive Waste Management Agency) envisages the safe disposal of High-Level Waste (HLW) and Intermediate-Level Long-Lived Waste (IL-LLW) in deep geological storage using a multi-barrier system. To ensure the containment of radioactivity, the principle of ... Mehr lesen
Olkiluoto at Eurajoki has been selected as the final repository site for spent nuclear waste in Finland. This area has been affected, at regional scale, by land-uplift processes related to the ice withdrawal. These events have resulted in a complex and stratified heterogeneous ... Mehr lesen