Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
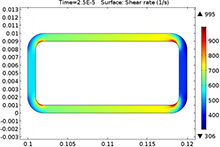
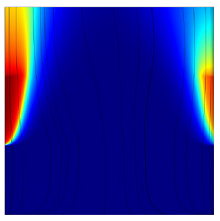
Introduction Present paper gives a comparison of the Upperconvected Maxwell (UCM) and the Oldroyd-B model for the calculation of dissipation in high shear-rate cases of viscodampers. When polymeric liquid is considered that part of energy that is irreversible can not be calculated in the ... Mehr lesen
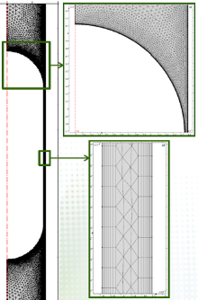
Plasma torches are used in processing of materials and in energy industry for producing plasma. In a non-transferred arc plasma torch, an electric arc can be glowed by applying a direct current (DC) between the cathode and anode, both placed inside the torch. Then, the plasma (Fig. 1) is ... Mehr lesen
Metal foams are interesting materials with many potential applications. Foamed metals or alloys include gas voids in the material structure and therefore the density is introduced as a new variable, with the real possibility to modify ad hoc their physical properties. In the indirect ... Mehr lesen
Intervertebral discs (IVD) are fibro-cartilages situated between vertebrae providing their joint flexibility. They play a major role in the transmission and absorption of load through the spine. The disc can undergo progressive structural and quantitative changes in its composition and ... Mehr lesen
Introduction Droplet-based microfluidics is a large source of research for scientists of new biotechnologies, aerosols or other 2D-Microfluidics devices. Here, we will focus on an industrial application of a 3D microfluidic device : the PH2DG, Pneumo-HydroDynamic Droplet Generator. The ... Mehr lesen
The dependency of electrochemical processes performances on mass transfer is well-known. Electrolyte flow in the vicinity of electrodes surface can enhance reactions due to increased mass transfer. This flow can be generated by the production of a gaseous phase, leading to a natural ... Mehr lesen
Recently, due to the dynamically increasing complexity of modern systems, a strong necessity appears for more systematic approaches to high quality control and process monitoring. Requirements imposed by process control in the area of spatio-temporal physical systems also called ... Mehr lesen
The use of microwaves for heating purposes of dielectric materials is encountered in many industrial applications (food processing, chemistry, material engineering and medical applications). In most of these thermal applications, the prediction of the temperature evolution within the ... Mehr lesen
In the present work, numerical simulations of a Monolith Reactor (MR) are carried out in order to develop a pre-design tool for industrial-scale reactors applied to highly exothermal reactions. The reacting circular channels (2-4 mm internal diameter) are coated with a few micron thick ... Mehr lesen
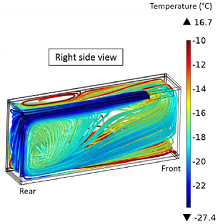
Heat transfer inside a refrigerated truck is a key phenomenon that governs the temperature inside the truck and the regulation of the cooling system. Up to now, a lot of experimental studies ([Tso et al., 02]) have been carried out to assess the effect of opening the door and to minimize ... Mehr lesen