Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
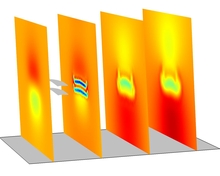
The CWRU Turbine is a research turbine located in a urban campus in Cleveland, Ohio. This location may create turbulence, resulting in a possible loss in energy generation. This research attempts to answers the question of whether the wind flow is affected by the buildings or not. The ... Mehr lesen
Dilution’s issue during dry machining have raised the interest’s environmental researchers and engineers. In fact, the sampling of dust emitted during dry machining was a serious problem for air quality evaluation at the workplace. Furthermore, the best sampling of fine and ultrafine ... Mehr lesen
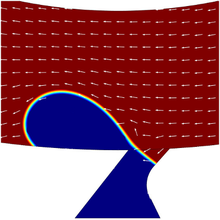
The hydraulic flocculates are employed in water treatment plants (WTPs), but may present problems during the mixing stage reducing the efficiency of treatment. In this context modeling of a hydraulic flocculate using COMSOL and a 1:10 scale model of the Maringá-PR Brazil city WTP ... Mehr lesen
Heat sinks for cryogenic applications using helium gas as the coolant are not readily available. They require to be designed specifically for the intended application. A finite element model was developed to study the feasibility and optimize the design. The FEM computing package COMSOL ... Mehr lesen
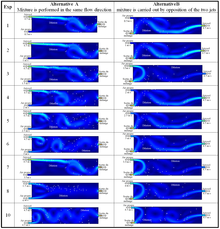
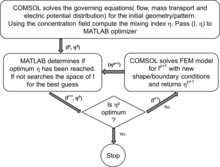
The performance of a homogeneous T-mixer can be enhanced significantly by the stimulation of secondary/ transverse flows in the microchannel. Various mixing mechanisms are reported for enhancing micromixing performance such as grooves at the channel bottom, heterogeneous charge patterns ... Mehr lesen
COMSOL Multiphysics software was used to structurally optimize the Wright brothers’ flyer. The flyer was drawn in SolidWorks, imported and meshed in COMSOL. COMSOL Solid Mechanics module was used to analyze the flyer. Four of the sixteen struts were removed yet the structural ... Mehr lesen
Whilst initially developed as a diagnostic aid to improve echogenicity in ultrasound imaging, gas-filled lipid microbubbles are now emerging as a next generation \'theranostic\' tool in the medical arena. Here, their therapeutic potential has now been realized through their unique ... Mehr lesen
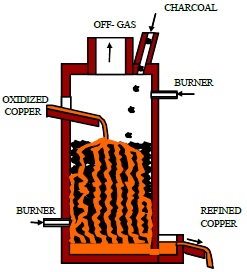
Throughout history, the copper pyrometallurgical processes have been carried out mostly in discontinuous or batch systems. In recent decades new continuous technologies have been developed but focused only on Smelting and Converting stages leaving aside the Refining one. In 2002 a novel ... Mehr lesen
This paper describes the development of a COMSOL model of Electro-Chemical-Mechanical Planarization (ECMP) that was validated with experimental data. ECMP is used for processing of semiconductor wafers. We developed a 2D model of flow of phosphoric acid solution (the electrolyte) between ... Mehr lesen
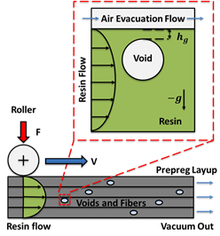
Voids in composite materials can lead to degraded structural performance. The following is a study of voids or bubbles in uncured viscous polymer resin during composites processing. The goal is to determine if voids can successfully migrate towards vacuum pathways, coalesce with the ... Mehr lesen