Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
Vorticella convallaria, a sessile peritrich ciliate having a contractile stalk, is regarded as a model biological spring because of its remarkably fast contraction. Because the cell body shrinks to sphere-like shape during contractions, it can be assumed to be a sphere moving in ... Mehr lesen
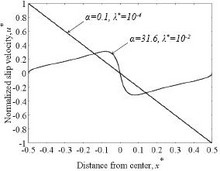
We present a numerical model for simulating highly nonlinear electrokinetic phenomena, which occurs at high zeta potentials. In this model, the electric double layer is realized by solving a partial differential equation (PDE) on the double-layer-inducing surface. We also allow for a ... Mehr lesen
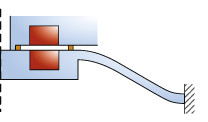
This paper describes the design of a normally closed, electrodynamic microvalve. Magnetic forces between a permanent magnet in the valve cover and a soft magnet in the valve seat hold the valve closed. The combination of electrodynamic actuation and a mechanical restoring spring are ... Mehr lesen
Transport phenomena in spatially periodic magnetic systems, in particular the directed transport of magnetic beads in a so called magnetic ratchet (Brownian motor) are considered. Simulations are carried out to test and optimize this system, where the Smoluchowski equation with flux ... Mehr lesen
This paper presents a methodology towards designing, analyzing and optimizing piezoelectric interdigitated microactuators using COMSOL Multiphysics. The models used in this study were based on a circularly interdigitated design that takes advantage of primarily the d{;sub}33 ... Mehr lesen
COMSOL Multiphysics software, when properly configured, can readily solve modeling problems in the laminar flow regime using the standard Navier-Stokes equations or in the fully turbulent flow regime using the kappa-epsilon model. Failure to solve a particular model is typically ... Mehr lesen
Damping is the liminting factor for the reachable maximum deflection. Thus, it is a very important issue for resonant microsystems. In this paper, we present a damping model for out-of-plane comb driven resonant micromirrors. The basic concept of this model is to attribute viscous ... Mehr lesen
The objective of this work has been to realize a feasibility study of a cooling device for a SQUID sensor using liquid nitrogen flowing through micro channels. The design consists of an epoxy cylindrical vacuum vessel skewed by a silicon microchannel heat sink. The SQUID sensor is ... Mehr lesen
Electrowetting occurs with the electrical control of the surface wetting properties through the application of an electric potential. A simulation of electrowetting driven droplet dynamics is performed using the COMSOL Multiphysics level-set method for a sessile droplet and for a ... Mehr lesen
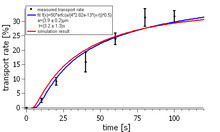
We have implemented a two dimensional chromatography model for the analysis and optimization of structured micro pillar arrays. Dynamic surface interaction of solved molecules is taken into account by the kinetic Langmuir model. Variations of the pillar array geometry lead to deviations ... Mehr lesen