Spanwise Rotating Turbulent Channel Flow
Application ID: 143741
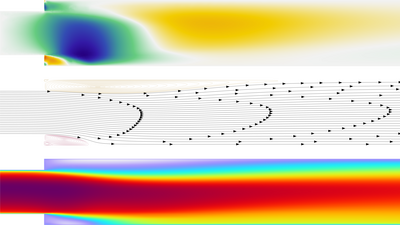
The Turbulent flow, Elliptic Blending R-ε interface is used to analyze fully developed turbulent flow in a spanwise rotating channel. Due to the influence of the Coriolis force on turbulence, profiles of the flow variables are skewed at moderate rotation rates. An asymmetry between the cyclonic (stable) and anticyclonic (unstable) sides of the channel is observed. The velocity gradient is stronger at the unstable side, with higher turbulence level and higher friction velocity at the corresponding wall. Meantime, the maximum peak of the velocity is shifted to the stable side. At higher rotation rates, the flow starts to relaminarize, and attains a symmetric Poiseuille profile at sufficiently high rotation rates.
Channel flow with a sudden expansion exhibits two primary recirculation bubbles (each complemented by a secondary counter-rotating recirculation bubble). Moderate frame rotation reduces the length of the bubble on the unstable side, and increases the length of the bubble on the stable side.
The Elliptic Blending R-ε turbulence model is able to capture the rotation rate dependence of most features of the rotating channel flow, especially the flow characteristics at the unstable side. It also correctly describes the phenomena at the unstable side of the rotating channel flow with a sudden expansion, such as the peak of the friction velocity and the recirculation length, although the recirculation length at the stable side is overestimated.
Dieses Beispiel veranschaulicht Anwendungen diesen Typs, die mit den folgenden Produkten erstellt wurden:
Allerdings können zusätzliche Produkte erforderlich sein, um es vollständig zu definieren und zu modellieren. Weiterhin kann dieses Beispiel auch mit Komponenten aus den folgenden Produktkombinationen definiert und modelliert werden:
Die Kombination von COMSOL® Produkten, die für die Modellierung Ihrer Anwendung erforderlich ist, hängt von verschiedenen Faktoren ab und kann Randbedingungen, Materialeigenschaften, Physik-Interfaces und Bauteilbibliotheken umfassen. Bestimmte Funktionen können von mehreren Produkten gemeinsam genutzt werden. Um die richtige Produktkombination für Ihre Modellierungsanforderungen zu ermitteln, lesen Sie die Spezifikationstabelle und nutzen Sie eine kostenlose Evaluierungslizenz. Die COMSOL Vertriebs- und Support-Teams stehen Ihnen für alle Fragen zur Verfügung, die Sie diesbezüglich haben.



