Sehen Sie, wie die Multiphysik-Simulation in verschiedenen Branchen eingesetzt wird
Multiphysik-Modellierung und -Simulation treiben Innovationen in Industrie und Wissenschaft voran – wie die zahlreichen Anwendungsbeispiele zeigen, die jedes Jahr in den Fachbeiträgen und Postern von Ingenieuren, Forschern und Wissenschaftlern auf der COMSOL Conference vorgestellt werden. Lassen Sie sich von den unten aufgeführten aktuellen Beiträgen inspirieren oder nutzen Sie die Schnellsuche, um eine bestimmte Präsentation zu finden oder nach Anwendungsbereich oder Konferenzjahr/-ort zu filtern.
Sehen Sie sich die Kollektion für die COMSOL Conference 2024 an
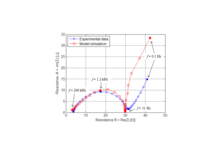
This study demonstrates that a multiphysics model of a LiFePO4/Li half-cell can be applied to simulate the impedance results from an EIS. However, it implies that the double layer capacitance has to be taken into account, since it is responsible of the semi-circle in the impedance ... Mehr lesen
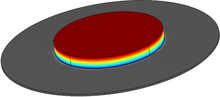
The tertiary current distributions on the wafer in a plating cell are studied in this work. An acid copper sulfate electrolyte composed of CuSO4/5H2O of 2.4 g/L and H2SO4 of 90 g/L is taken into account for copper deposition on the wafer. The solution of shear-plate agitating fluid ... Mehr lesen
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) are electrochemical conversion devices that utilize ceramics as their electrolyte material for oxygen conduction. Compared to other types of fuel cells, they operate at relatively high temperatures, typically 400°C to 1000°C, and have an electrical ... Mehr lesen
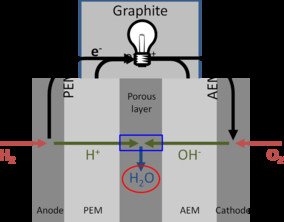
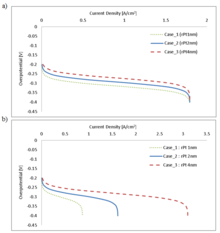
The Polymer Electrolyte Membrane fuel cell is one of the most promising green technologies for addressing portable, as well as transportation power needs. However, the science behind the fuel cell, in many regards, is still an enigma, and even more so, with the vast numbers of novel ... Mehr lesen
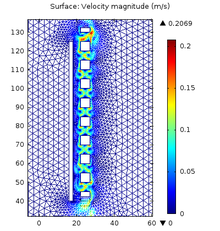
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling is a useful tool to gain an insight into various high temperature metallurgical processes such as the magnesium refining and the magnesium solid oxide membrane (SOM) electrolysis. In both processes, argon gas was used to stir the molten salt ... Mehr lesen
We have started constructing preliminary design COMSOL models of a bacteriologically driven \'fuel cell\' that is intended to process waste products, such as carbon dioxide and brine, from a crewed vehicle. At this early stage, this complex system is reduced to two electrodes separated ... Mehr lesen
Fuel cells are devices that convert chemical energy of a fuel into electrical energy through electrochemical processes. One of the types of fuel cell is the Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) that uses solid ceramics for electrolytes. Numerical simulation involves constructing a mathematical ... Mehr lesen
Introduction: Understanding the mass and charge transport behavior of heterogeneous systems that include diffusion, migration, and reaction of ions is important in fuel cells, batteries, and other electrochemical applications. Here, a numerical model for charged species transport and ... Mehr lesen
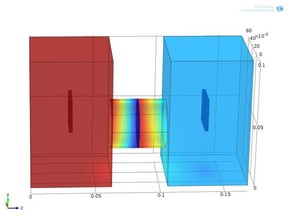
Pitting corrosion is a complex phenomenon where rates of: i) chemical reactions, ii) diffusion of various species involve in those reactions, and iii) species dissolution at the metal-electrolyte interface are fully dependent on each other, except under special conditions or assumptions. ... Mehr lesen
In this study, the basic catalyst layer (CL) structure, consisting of carbon-supported Pt particles (C|Pt) and an ionomer binder, is investigated numerically by using COMSOL. The significance of modeling discrete Pt particles on the carbon support is highlighted by comparing the cell ... Mehr lesen