Neuerungen im MEMS Module
Für Nutzer des MEMS Module bietet COMSOL Multiphysics® Version 6.4 eine automatische Kontaktmodellierung, Symmetrieunterstützung für Terminal und einen neuen Standardplot, der die gespeicherte Gesamtenergie zeigt. Weitere Informationen zu diesen Updates finden Sie unten.
Automatische Kontaktmodellierung mit vielen Objekten
Um Modelle mit einer Vielzahl möglicher Kontaktinteraktionen einfach erstellen zu können, wurde ein neues Feature General Contact eingeführt, das automatisch Kontaktbedingungen zwischen vielen Objekten festlegt.
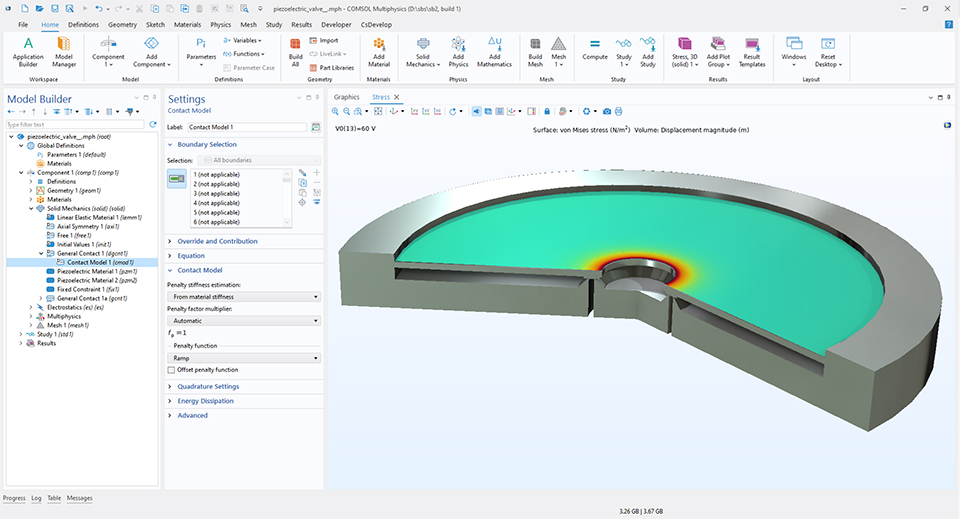
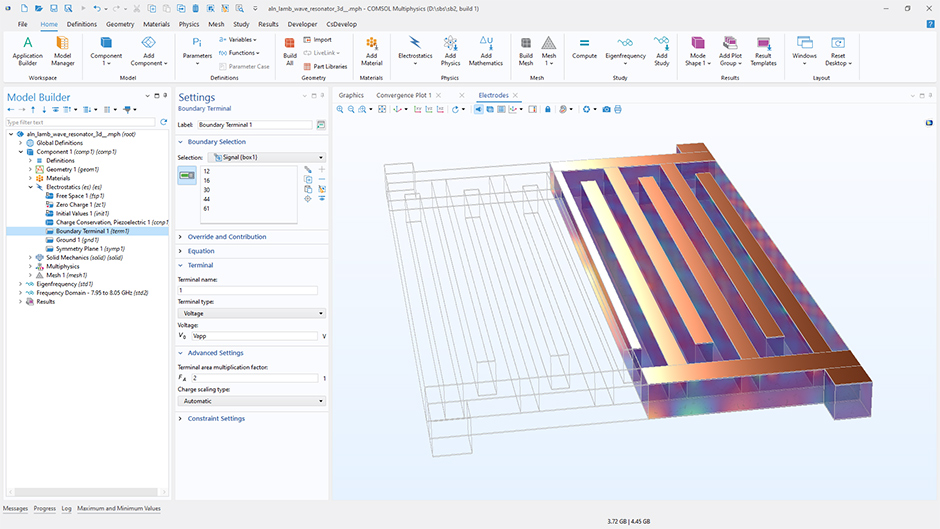
Symmetrie für Terminal
Das Feature Terminal unterstützt nun einen Flächenmultiplikationsfaktor (verfügbar im Abschnitt Advanced Settings nach Aktivierung der Advanced Physics Options). Dieser berücksichtigt die Symmetrie, indem er die Terminalfläche skaliert, sodass verbundene Schaltungen oder Lasten das gesamte Gerät erkennen, auch wenn nur ein Teil modelliert ist. Beispielsweise sollte ein Faktor von 2 verwendet werden, wenn das Modell die Hälfte des Geräts darstellt. Dieses Update ist für die Interfaces Electrostatics, Electric Currents und Magnetic and Electric Fields verfügbar.
Standardplot der Gesamtenergie
Um den Frequenzgang zu visualisieren und die Resonanzspitzen eines elektromechanischen Systems zu identifizieren, steht für Frequenzbereichsstudien mit einer Elektromechanik- oder einer Piezoelektrizitäts-Kopplung ein neuer Standardplot der gespeicherten Gesamtenergie, Wh_tot, zur Verfügung.
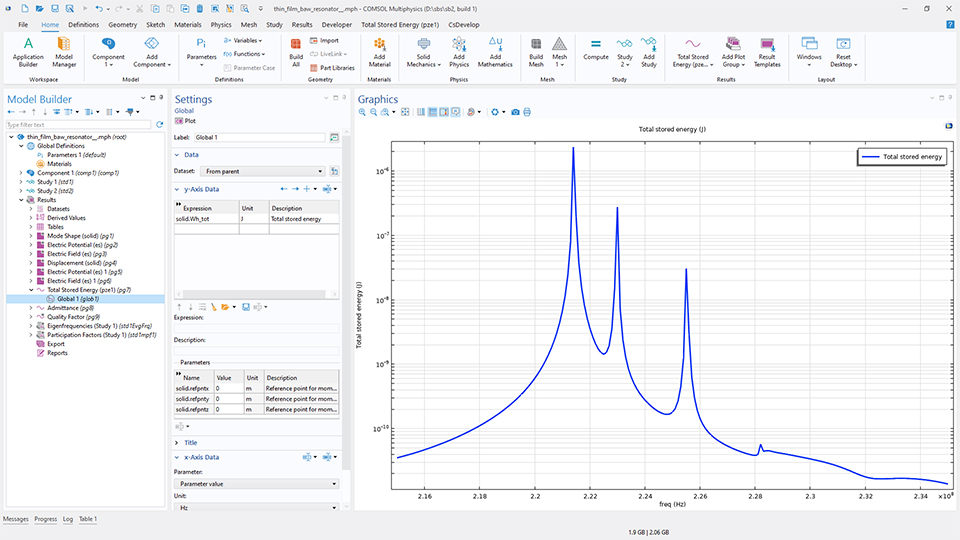
Wh_tot, erstellt. Das Standarddiagramm erfordert entweder die Kopplung Piezoelectricity oder die Kopplung Electromechanics.
Neue und aktualisierte Tutorial-Modelle
COMSOL Multiphysics® Version 6.4 enthält mehrere neue und aktualisierte Tutorial-Modelle für das MEMS Module.
Birdbath Resonator Gyroscope
Die achsensymmetrische Kuppelform des Resonators ermöglicht die Kopplung zwischen Antriebs- und Messmodus. Dieses Design minimiert Kosten, Gewicht, Größe und Stromverbrauch und bietet gleichzeitig eine höhere Genauigkeit und Stabilität. Dargestellt sind die Verschiebungsfelder mit (links) und ohne (rechts) Coriolis-Anregung, die zeigen, wie Winkelbewegungen eine messbare Verzerrung erzeugen.
Velocity Calculation for SAW Unit Cell
Dieses Modell berechnet die Geschwindigkeit der akustischen Oberflächenwelle (SAW) und zugehörige Parameter, wie beispielsweise die elektromechanischen Kopplungskoeffizienten k2 und kp, für verschiedene Einheitszellenkonfigurationen des 128°-YX-geschnittenen LiNbO3-Kristalls. Diese Parameter sind für verschiedene analytische und semi-analytische Methoden zum Design von SAW-Bauelementen nützlich. Die Verschiebung und das elektrische Feld in x-Richtung sind dargestellt.
Uncertainty Quantification Analysis of Piezoelectric Energy Harvester

piezoelectric_energy_harvester_uncertainty_quantification
Download aus der Application Gallery
SAW Euler Angle Rotation
Dieses Modell veranschaulicht, wie Euler-Winkelrotationen angewendet werden, um die Standard-Materialeigenschaften zu modifizieren, wenn keine schnittspezifischen Daten verfügbar sind. In diesem Beispiel werden drei Konfigurationen des 128°-YX-geschnittenen LiNbO3 verwendet, um Eigenfrequenzen und Eigenmoden zu berechnen. Dargestellt sind die Verschiebung und das Potential (links) sowie die Verschiebung und die piezoelektrische Dehnung (rechts) in x-Richtung.
Shape Optimization of Microphone Diaphragm
Dieses Tutorial-Modell veranschaulicht, wie die Studie Shape Optimization zur präzisen Abstimmung der Eigenfrequenz einer MEMS-Mikrofonmembran eingesetzt werden kann. Es werden die Veränderungen der Form der Federaufhängung dargestellt, wenn die Eigenfrequenz von 145 kHz auf 115 kHz gesenkt wird.
microphone_diaphragm_shape_optimization
Download aus der Application Gallery



