Neuerungen im Optimization Module
Für Nutzer des Optimization Module bietet COMSOL Multiphysics® Version 6.4 Stoppbedingungen für zeitabhängige Optimierungen, einen Studienschritt für die Parameteroptimierung und mehrere neue Tutorial-Modelle. Weitere Informationen zu den Updates finden Sie unten.
Zeitabhängige Optimierung
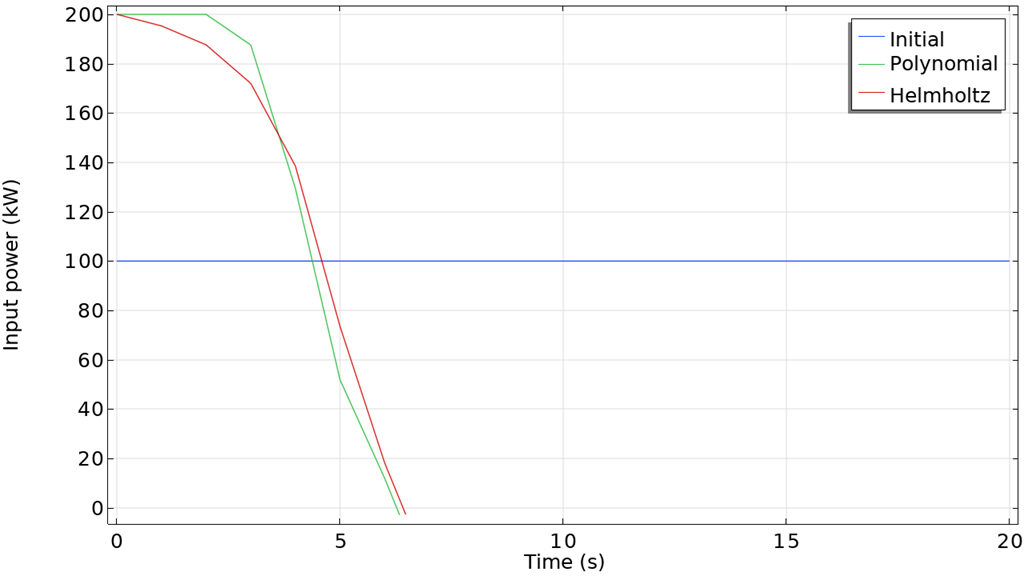
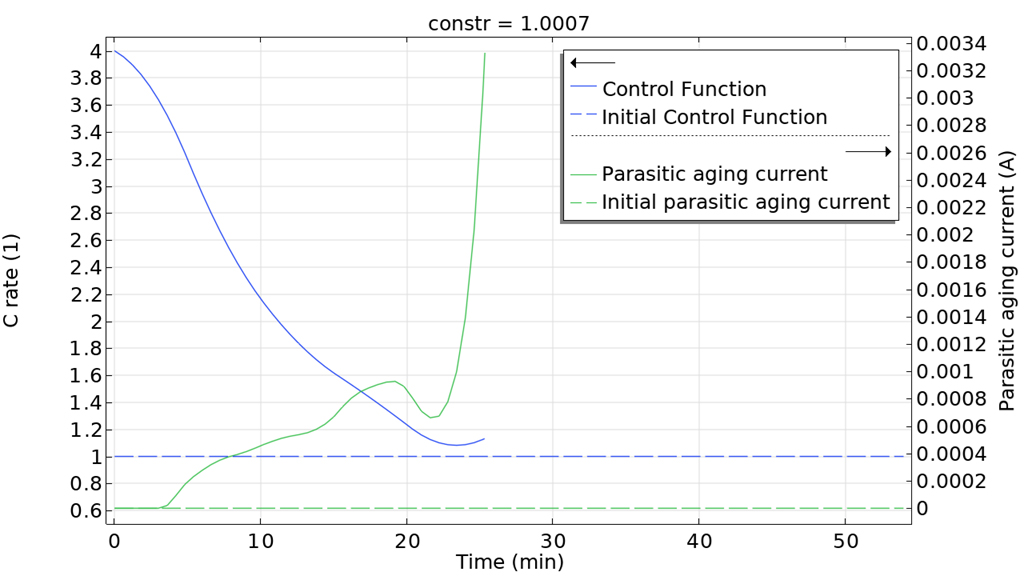
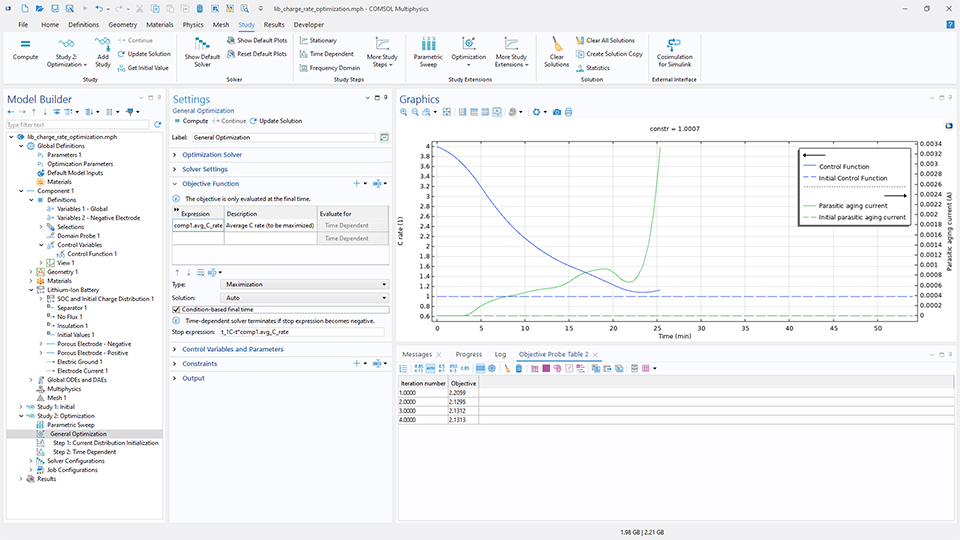
Die gradientenbasierte Optimierung für zeitabhängige Probleme kann nun auch zur Optimierung der Endzeit verwendet werden. Dies bedeutet, dass es möglich ist, entweder die Dauer eines Prozesses zu minimieren oder den Löser die Zeit wählen zu lassen, die den besten Zielwert liefert. Im folgenden Beispiel besteht das Ziel darin, die Ladezeit für eine Lithium-Ionen-Batterie zu minimieren. Das Modell verwendet das Feature Control Function, das nun den Export des optimierten Ergebnisses entweder als analytische Funktion oder als Interpolationsfunktion unterstützt.
Parameteroptimierung
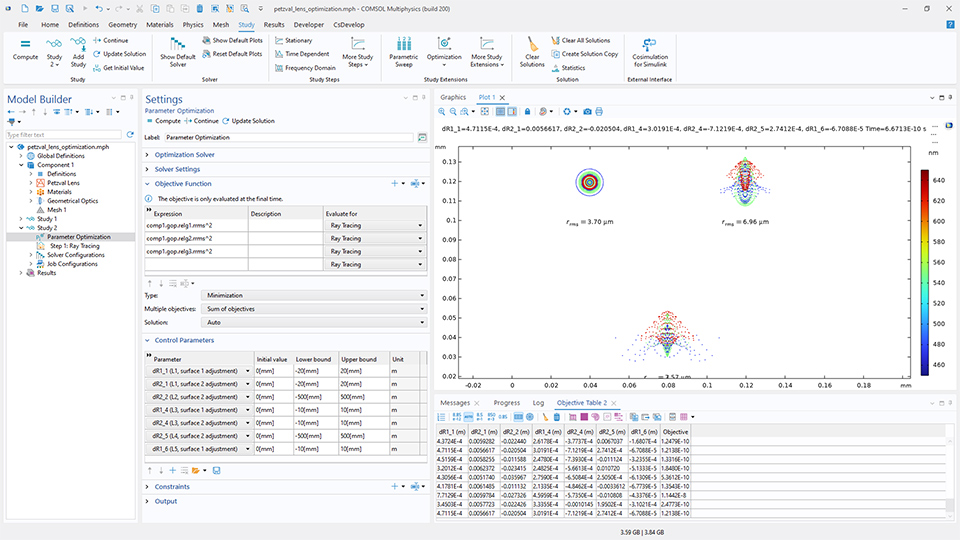
Es wurde ein speziell für die gradientenfreie Optimierung entwickelter Studienschritt Parameter Optimization eingeführt, bei dem die Skalierung der Kontrollparameter auf der Grundlage der Schranken festgelegt werden, sodass keine manuelle Definition mehr erforderlich ist. Das Feature unterstützt auch die automatische Erstellung neuer Parameterfälle auf der Grundlage der optimierten Parameter.
Darüber hinaus wurde die Benutzeroberfläche im Vergleich zum alten Studienschritt Optimization, der in General Optimization umbenannt wurde, neu organisiert. Der Studienschritt General Optimization und der Studienschritt Parameter Optimization unterstützen beide die Randomisierung der Anfangswerte für begrenzte globale Kontrollparameter, sodass verschiedene lokale Minima identifiziert werden können.
Gradientenbasierte Optimierungslöser
Der Optimierungslöser SNOPT wurde eingestellt; ältere Modelle wurden zu IPOPT migriert, das nun die empfohlene Methode zur Erzielung quadratischer Konvergenz darstellt (mit Ausnahme der Parameterschätzung, bei der der Löser Levenberg–Marquardt voraussichtlich überlegen ist). Darüber hinaus führte die Auswahl der Option MMA in einem Optimierungsstudienschritt früher zur Verwendung von GCMMA (für die Standard-Löserkonfiguration), während jetzt sowohl MMA als auch GCMMA auf Studienebene verfügbar sind.
Weitere neue Features und Verbesserungen
- Neue Features P-norm und Standard Deviation
- Das Feature P-norm kann den Maximalwert eines Feldes auf eine Weise approximieren, die mit der gradientenbasierten Optimierung kompatibel ist, wie sie häufig für Spannungsbeschränkungen in Strukturproblemen verwendet wird.
- Das Feature Standard Deviation kann verwendet werden, um ein Feld über eine Auswahl hinweg zu homogenisieren.
- Dem Interface Electromagnetic Waves wurden Fernfeldoperatoren hinzugefügt, die mit der gradientenbasierten Optimierung kompatibel sind.
- Die Optimierung von Eigenwerten unterstützt nun die Verwendung nicht-analytischer Operatoren im Zielausdruck, sodass es möglich ist, nur unter Berücksichtigung des Realteils für eine Ziel-Eigenfrequenz zu entwickeln.
- Das Feature Density Model unterstützt nun auch Extrusionsbeschränkungen.
- Leistungsverbesserungen für die gradientenbasierte Optimierung
Neue und aktualisierte Tutorial-Modelle
COMSOL Multiphysics® Version 6.4 enthält mehrere neue und aktualisierte Tutorial-Modelle für das Optimization Module.
Time-Optimal Control for Heating of a Rod
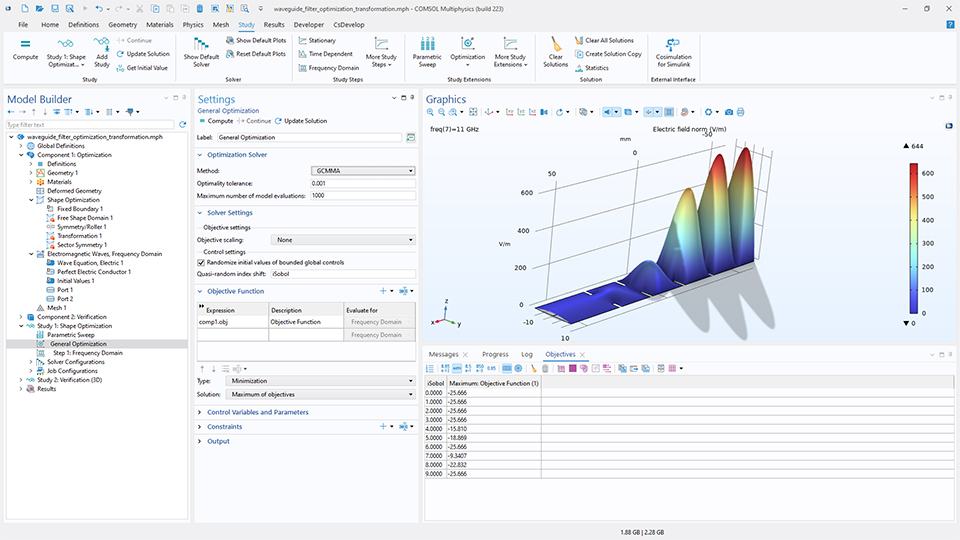
Designing a Metasurface Beam Deflector Using Shape Optimization
metasurface_beam_deflector_optimization
Download aus der Application Gallery
Minimizing the Charging Time of a Lithium-Ion Battery
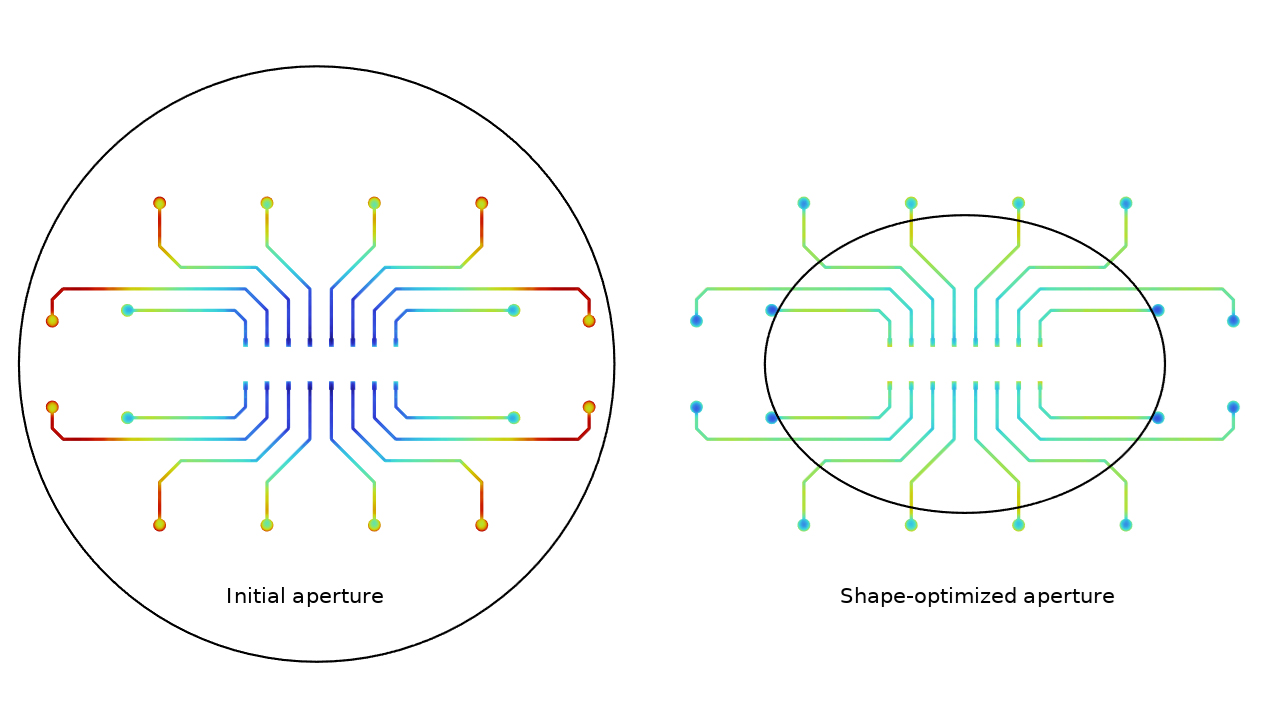
Aperture Shape Optimization for Electroplating of a Printed Circuit Board
Wheel Rim — Stress Optimization with Fatigue Evaluation
Topology Optimization of a Metalens
Minimizing the Drying Time of a Wood Particle
superheated_steam_drying_optimization
Download aus der Application Gallery